|
Ningbo Yinzhou Hongyong Machinery Factory
|
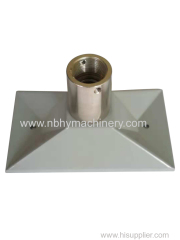
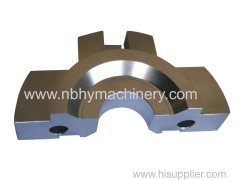
CNC Machining Auto/Car/Truck/Tractor/Ship Engine Parts with Metal Processing
| Price: | 15.3 USD |
| Payment Terms: | T/T,L/C |
| Place of Origin: | Zhejiang, China (Mainland) |
|
|
|
| Add to My Favorites | |
| HiSupplier Escrow |
Product Detail
CNC Machining Auto/Car/Truck/Tractor/Ship Engine Parts with Metal Processing
| 1 | Business Type: | OEM& ODM Manufacturer |
| 2 | Products Range: | Auto /Moto Parts, Machinery Parts, Hardware Accessories, Furniture Hardware etc |
| 3 | Materials: | Aluminum: AL6061, AL6082, AL7075, AL5052, etc |
| Steel: S355ML, S420ML, P20, SKD11, SKD61, SKH9, SKH51, S45C, etc | ||
| Iron: 1C45, Y15, C1211, SUM2212L14, 1215, etc | ||
| Stainless steel: SUS304, SUS303, SU316L, SUS440C, etc | ||
| 4 | Machining: | cleaning, turning, milling, drilling, grinding ,CNC shearing,laser cutting, welding etc |
| 5 | Surface Treatment: | Polishing, Deburring, Chrom Plate, Ni Plated, Zine plated, Silver platinng |
| Clear anodizing, Anodizing black, Carburizing Nitriding, Heat Treatment, etc | ||
| 6 | Testing Equipment: | Hexagon CMM, TESA Height Gauge, Projector, Micrometer, etc |
| 7 | QC System: | 100% Inspection before shipment |
| 8 | Payment Term: | T/T, L/C, D/P |
| 9 | Trade Terms: | FOB, CIF |
| 10 | Delivery Time: | 20-30Days(According to The Order) |
| 11 | Our Advantages: | Reliable Quality |
| Competitive Price | ||
| High precision, high quality, tight tolerance | ||
| Continuous Improvement | ||
| On-Time Delivery | ||
| Customer Satisfaction | ||
| Excellent After-Sales Service |
Our Factory

What are the common methods and techniques used in metal parts processing?
Machining:
Turning: Involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to create cylindrical components.
Milling: A cutting tool removes material by moving in various directions to produce complex shapes, including slots, holes, and contours.
Drilling: Drills create holes in metal components, and the process can vary from simple hole drilling to more complex operations like counterboring and countersinking.
Grinding: Abrasive wheels are used to achieve precise dimensional tolerances and surface finishes on metal parts.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Utilizes electrical discharges to remove material from the workpiece in highly accurate and intricate patterns.
Forming:
Stamping: A mechanical press is used to shape metal into specific forms or cut it into desired shapes.
Bending: Metal sheets or bars are bent using press brakes to create components with angular or curved shapes.
Extrusion: Metal is forced through a die to produce continuous shapes with a uniform cross-section.
Casting:
Die Casting: Molten metal is injected into a mold cavity to produce high-precision, near-net-shape components.
Sand Casting: Involves creating a mold by compacting sand around a pattern to form metal parts.
Investment Casting: A wax pattern is used to create a ceramic mold for casting intricate and complex metal components.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
Layer-by-layer additive manufacturing methods, such as selective laser melting (SLM) or fused deposition modeling (FDM), create metal parts directly from digital designs. This allows for highly customized and complex shapes.
Welding:
Welding methods, including MIG, TIG, and arc welding, are used to join metal components together, providing strength and structural integrity.
Laser Cutting and Waterjet Cutting:
Laser cutting uses a focused laser beam to cut through metal sheets or tubes with precision.
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water and abrasive materials to cut through metal, suitable for a wide range of materials.
Powder Metallurgy:
Involves compacting metal powders into the desired shape and then sintering them to create solid metal components with intricate details.
Heat Treatment:
Metal parts are subjected to controlled heating and cooling processes to modify their mechanical properties, such as hardness and toughness.
Surface Finishing:
Techniques like electroplating, anodizing, and powder coating are used to enhance the appearance and protect the surface of metal components.
The choice of method or technique depends on factors such as the type of metal, the complexity of the part, required tolerances, production volume, and cost considerations.
What quality control measures are typically implemented in metal parts processing to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the finished components?
Quality control measures in metal parts processing are essential to ensure the accuracy and integrity of finished components. The quality control measures include:
Dimensional Inspection:
The use of precision measuring tools like calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) to verify the dimensions and tolerances of metal parts.
Visual Inspection:
Visual inspection is performed to identify surface defects, such as cracks, scratches, burrs, and irregularities.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Techniques like ultrasonic testing, X-ray inspection, and dye penetrant testing are used to detect hidden defects within the material without causing damage.
Material Analysis:
Material composition and properties are analyzed using techniques like spectroscopy and hardness testing to verify that the correct material has been used and that it meets required specifications.
In-Process Inspection:
Regular inspections during the manufacturing process to catch and correct issues as they arise, minimizing the risk of producing out-of-spec components.
Statistical Process Control (SPC):
Monitoring and controlling the production process using statistical techniques to ensure that it remains within acceptable limits.
First Article Inspection (FAI):
A comprehensive inspection of the first produced part to validate that it meets all design requirements and serves as a reference for the production run.
Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility (GR&R):
A measurement system analysis to determine the reliability of measuring equipment and the consistency of measurement results.
Supplier Audits and Qualification:
Regular audits and assessments of suppliers and subcontractors to ensure that they meet quality and safety standards in their manufacturing processes.
Process Controls:
Strict control of the manufacturing process, including parameters like temperature, pressure, and cutting speeds to maintain consistency and precision in production.
Final Inspection and Testing:
A final inspection is conducted to verify that all parts meet quality standards before they are shipped or used in assembly.
What are the key considerations when selecting a metal parts processing method for a automobile industry?
The key factors to consider are:
Material type
Material Compatibility
Material properties
Tolerances and Accuracy
Surface finish
yield
Production scale
scale economy
The complexity of components
Lead time and speed
Prototyping and Production
environmental effect
Cost considerations